WAN
Wide Area Network (WAN)
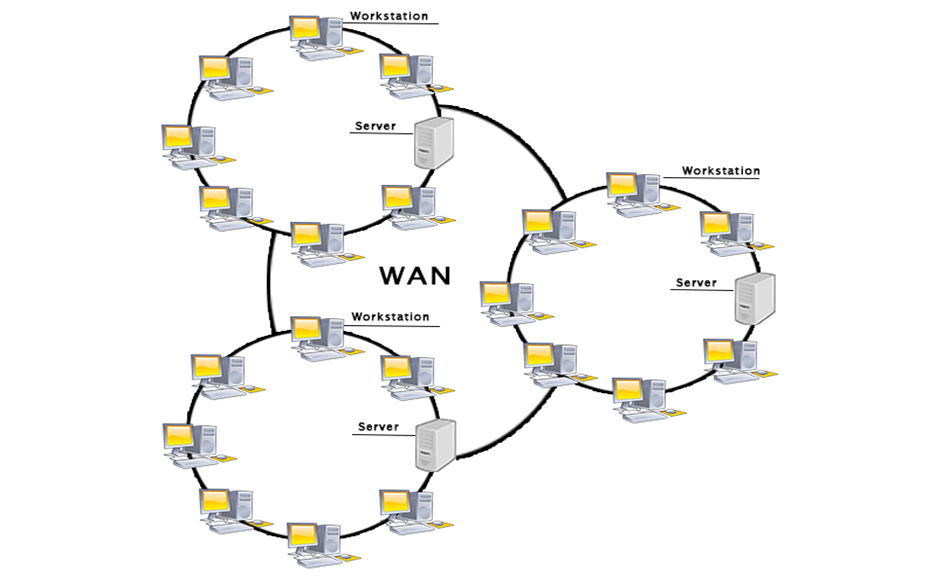
WAN or Wide Area Network is a computer network that extends over a large geographical area, although it might be confined within the bounds of a state or country. A WAN could be a connection of LAN connecting to other LAN’s via telephone lines and radio waves and may be limited to an enterprise (a corporation or an organization) or accessible to the public. The technology is high speed and relatively expensive.
There are two types of WAN: Switched WAN and Point-to-Point WAN. WAN is difficult to design and maintain. Similar to a MAN, the fault tolerance of a WAN is less and there is more congestion in the network. A Communication medium used for WAN is PSTN or Satellite Link. Due to long distance transmission, the noise and error tend to be more in WAN.
WAN’s data rate is slow about a 10th LAN’s speed, since it involves increased distance and increased number of servers and terminals etc. Speeds of WAN ranges from few kilobits per second (Kbps) to megabits per second (Mbps). Propagation delay is one of the biggest problems faced here. Devices used for transmission of data through WAN are: Optic wires, Microwaves and Satellites. Example of a Switched WAN is the asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) network and Point-to-Point WAN is dial-up line that connects a home computer to the Internet.
- A Wide Area Network is a network that extends over a large geographical area such as states or countries.
- A Wide Area Network is quite bigger network than the LAN.
- A Wide Area Network is not limited to a single location, but it spans over a large geographical area through a telephone line, fibre optic cable or satellite links.
- The internet is one of the biggest WAN in the world.
- A Wide Area Network is widely used in the field of Business, government, and education.
Examples Of Wide Area Network:
- Mobile Broadband: A 4G network is widely used across a region or country.
- Last mile: A telecom company is used to provide the internet services to the customers in hundreds of cities by connecting their home with fiber.
- Private network: A bank provides a private network that connects the 44 offices. This network is made by using the telephone leased line provided by the telecom company.
Advantages Of Wide Area Network:
Following are the advantages of the Wide Area Network:- Geographical area: A Wide Area Network provides a large geographical area. Suppose if the branch of our office is in a different city then we can connect with them through WAN. The internet provides a leased line through which we can connect with another branch.
- Centralized data: In case of WAN network, data is centralized. Therefore, we do not need to buy the emails, files or back up servers.
- Get updated files: Software companies work on the live server. Therefore, the programmers get the updated files within seconds.
- Exchange messages: In a WAN network, messages are transmitted fast. The web application like Facebook, Whatsapp, Skype allows you to communicate with friends.
- Sharing of software and resources: In WAN network, we can share the software and other resources like a hard drive, RAM.
- Global business: We can do the business over the internet globally.
- High bandwidth: If we use the leased lines for our company then this gives the high bandwidth. The high bandwidth increases the data transfer rate which in turn increases the productivity of our company.
Disadvantages of Wide Area Network:
The following are the disadvantages of the Wide Area Network:
- Security issue: A WAN network has more security issues as compared to LAN and MAN network as all the technologies are combined together that creates the security problem.
- Needs Firewall & antivirus software: The data is transferred on the internet which can be changed or hacked by the hackers, so the firewall needs to be used. Some people can inject the virus in our system so antivirus is needed to protect from such a virus.
- High Setup cost: An installation cost of the WAN network is high as it involves the purchasing of routers, switches.
- Troubleshooting problems: It covers a large area so fixing the problem is difficult.